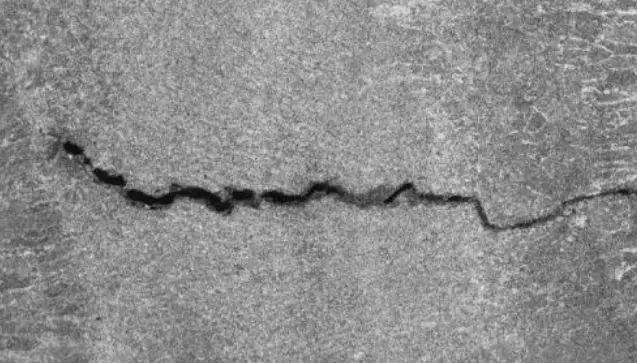
Casting internal stress exceeds the tensile strength of the metal, the casting will produce cracks. Divided into hot cracks and cold cracks.
- Thermal cracks
Thermal cracking is a casting in the late solidification at high temperatures along the grain boundaries of the formation of cracks.
Macro: oxidized color at the break; short cracks; wide dimensional gap (width 0.05~0.5mm); zigzag shape
Microscopic: distributed along the grain boundary, along the crystal (or intergranular) fracture.
Factors affecting the formation of thermal cracks
1) the casting alloy nature of the impact
Since the beginning of the line shrinkage temperature to the solid phase line between the effective crystallization interval is smaller then the absolute shrinkage of the alloy in this temperature range is smaller, the casting of the stress produced by the smaller, so the alloy formation of hot cracking tendency is smaller. The opposite is also true.
2) Types of alloying elements
Promote the formation of crystalline cracks – S, P, C, Ni
Inhibit the formation of crystalline cracks – Mn, Si, Ti, rare earth elements.
Sulfur and phosphorus – the most harmful impurity elements
Carbon – the main element affecting thermal cracking, exacerbating the harmful effects of sulfur, phosphorus and other elements.
Manganese – desulfurization effect + improves the morphology of sulfides, thin film-like changes to spherical, improves the resistance of the metal to cracking.
Prevention of thermal cracking
- Try to choose alloys with a small range of solidification temperatures and a small tendency to thermal cracking.
- The concessions of casting and core should be improved to reduce the mechanical stress.
- For cast steel and cast iron parts, the sulfur content must be strictly controlled to avoid the generation of FeS to prevent thermal embrittlement.
- Cold cracking
Cold cracking is the casting cooled to the elastic state, due to local casting stress is greater than the material strength limit and the cracking caused. Always occurs in the cooling process to withstand higher tensile stress parts, especially stress concentration parts. Large castings with uneven wall thickness and complex shapes are prone to cold cracks.
Characteristics:
- Passing through the intracrystalline and crystalline boundaries
- Small cracks
- In the form of a continuous straight line
- There is a metallic luster or slight oxidized color in the seam
Cold cracking prevention
1) Make the casting wall thickness as uniform as possible.
2) Adopt the principle of simultaneous solidification.
3) for cast steel and cast iron parts, must strictly control the content of phosphorus: to avoid generating Fe3P, to prevent cold embrittlement.